Human beings use languages to communicate with other humans. Animals also communicate verbally or non-verbally with each other. Let us imagine how computers or any other devices like mobile phones, laptops communicate with one other? All computing devices need specified #protocols/rules to communicate with one another and that is termed as #Network. The Network is framed based on reference models and one of the models is the OSI model.
What is OSI Model?
OSI is represented as Open Source Interconnection (OSI) reference model that forms a framework for designing a hierarchical architecture on a computing function for a network system.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) framed the #OSI model and published it in 1984. Though this model does not map to specific functionalities of the system, the OSI is the standard model used to frame the #architecture of the system networks. The OSI Model is divided into seven layers of operation based on the functions. In this article, let us explore the characteristics and different layers of the OSI Model.
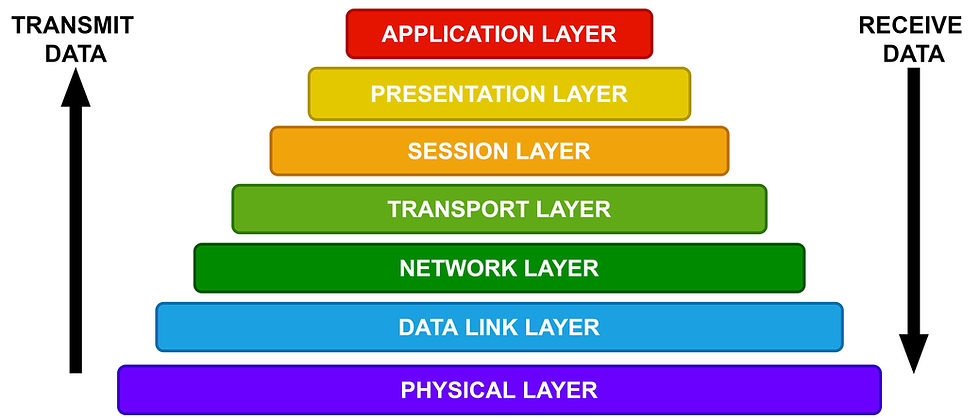
CHARACTERISTICS OF OSI MODEL
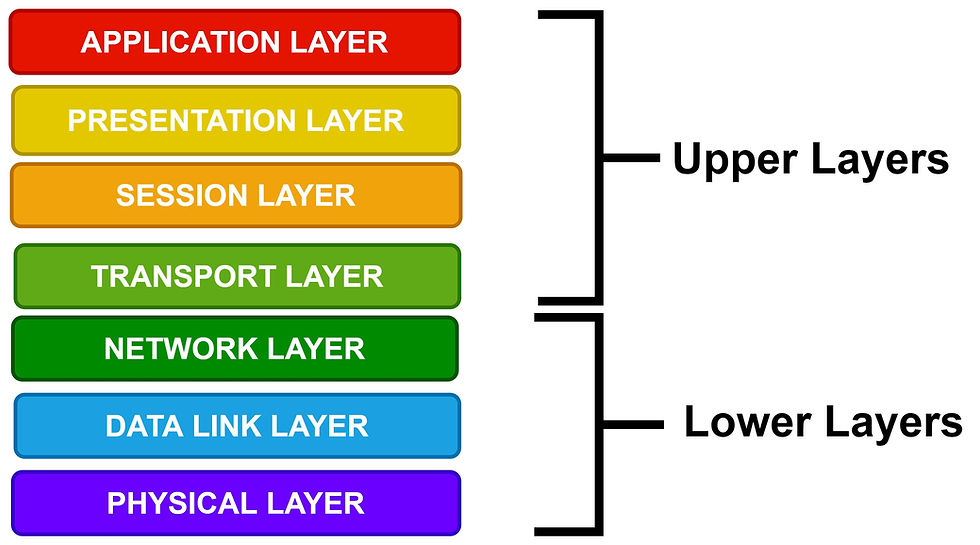
Based on the interaction of the system on the physical or application medium, the OSI model is divided into two group layers as Upper layers and lower layers.
The Upper Layers interacts only with the end-user. Hence it deals with problems related to the software side near the application layers.
The lower layers interact mostly with the physical medium of the device. But it deals with problems related to both the software and hardware side on the #transmission of data.
LAYERS OF OSI MODEL
The Hierarchical #architecture of the OSI model is classified into 7 layers to perform its identical task assigned to it. The seven layers are:
Physical layer
Data Link layer
Network layer
Transport layer
Session layer
Presentation layer
Application layer
Physical Layers:
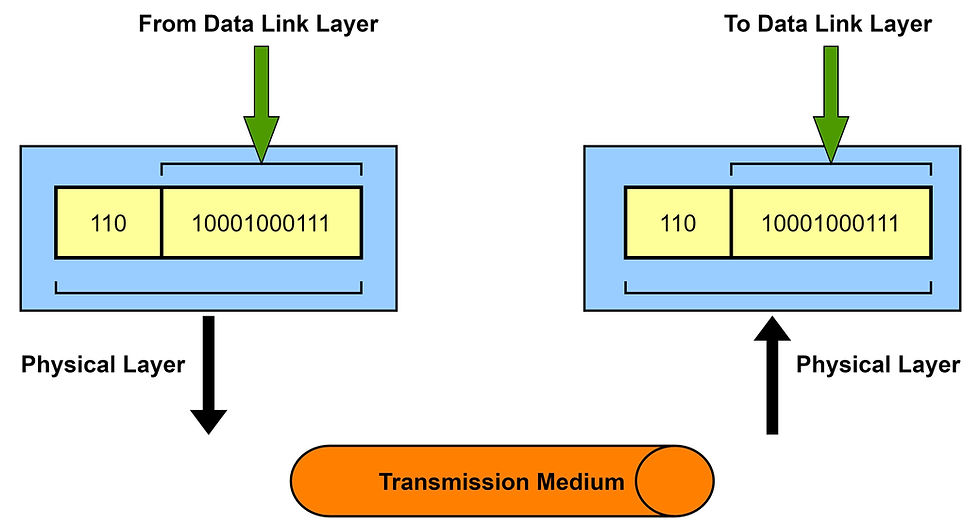
This is the lowest layer in the OSI model and establishes a physical connection between two devices. In this layer, the information is transferred in the form of bits from one node to another with specifications. The specifications of the physical layers are included in the standards of #Bluetooth, #Ethernet, and #USB. This layer can also be expressed in terms of network topology. Various functions of the #Physical layer are:
It synchronizes the provided data at bit level with the clock signal.
It controls the transmission rate of a bit per second.
It specifies the arrangement of nodes in the network topology.
It also determines how the data flows in the connected devices.
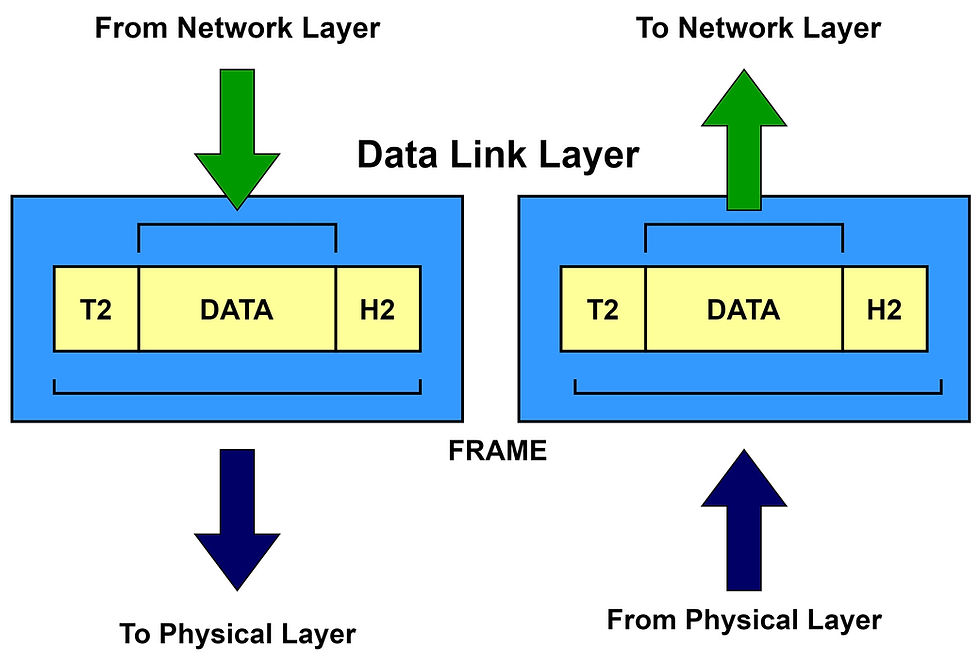
Data Link Layer:
The #Data Link layer is responsible for transferring errorless information on a node to node delivery between two physically connected devices. This layer defines the format in which the data can be transferred between the devices. Datalink layer is classified into two layers
Logical Link Control (LLC)Layer- transfers the packets to the network layer and controls the flow of the transmitted data.
Medium Access Control (MAC)Layer- forms a bridge between the LLC layer and the network physical layer.
The various functions of the Data Link layer are:
It converts the physical bits into a packet of information of frames.
It recognizes the address of the network layers from the header.
It controls the flow and error of the transmitted data.
It also determines the device access to the layer at a particular time.
Network Layer:
The #Network layer is the third layer in the OSI model, it is responsible for routing and transferring the packets functionally and methodically. This layer selects the right and shortest path to transfer the packets based on the network connection. The protocol that is framed to route the network traffic is called a network layer protocol, for example, #IP and #Ipv6. The various functions of the network layer are:
It chose the best path for the data to each destination. It is called routing.
It provides a logical connection between computing devices.
It addresses the source and destination from the header to identify the devices in the network.
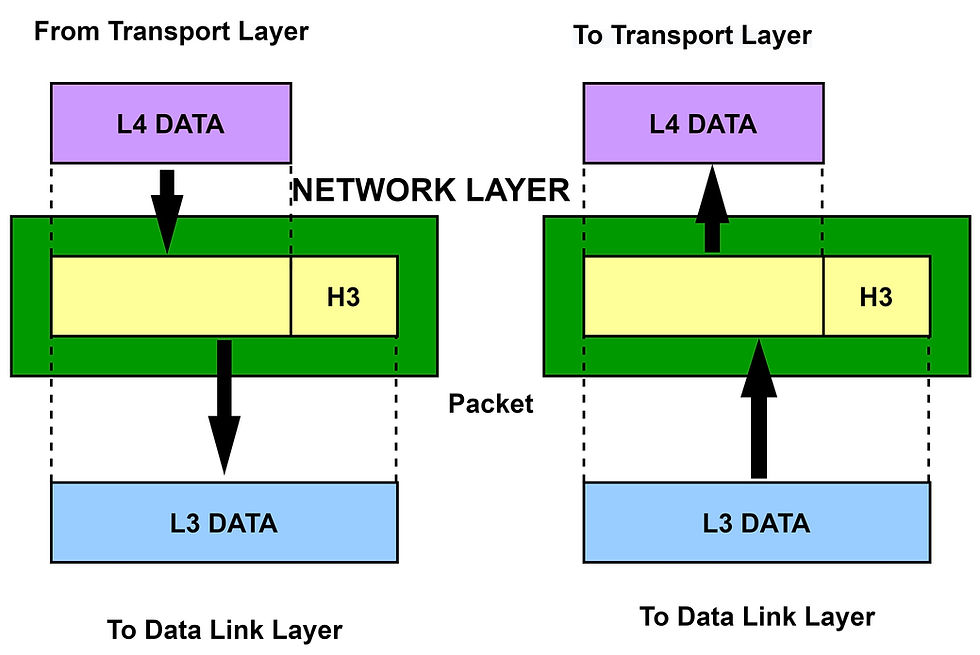
Transport Layer:
The Transport layer is responsible to transmit the information completely in an orderly manner without any duplication of information. The information in the transport layer is referred to in terms of segments. In this layer, two types of #protocols are used. They are:
Transmission Control Protocol transmits the segments through the internet by multiple routing to reach the destination.
User Datagram Protocol is a transport layer protocol, it does not produce an acknowledgment when the segment reaches the destination. This makes the protocol unreliable.
The Functions of the Transport layer:
This layer ensures the transmission of data from one system to another and the correct point of the process to be reached.
It divides the received data into several segments with unique identifiers, which helps to deliver the data to the correct destination.
It is also responsible for the flow and error-free transmission of the data.
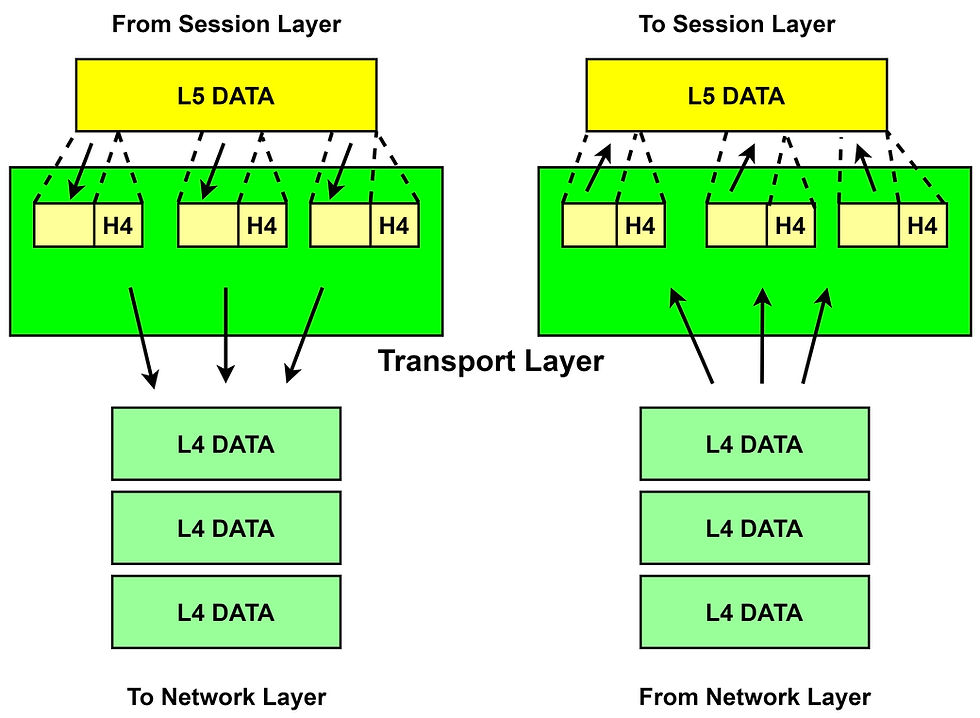
Session Layer:
The Session layer establishes, maintains, #authenticate, and provides security to the connection between two computers. The various function of the session layer are:
It allows communication between two processes that can be half-duplex or full-duplex.
It enables the recovery of missed data when an error occurs in transmitting the sequence of data at a time by #synchronization.
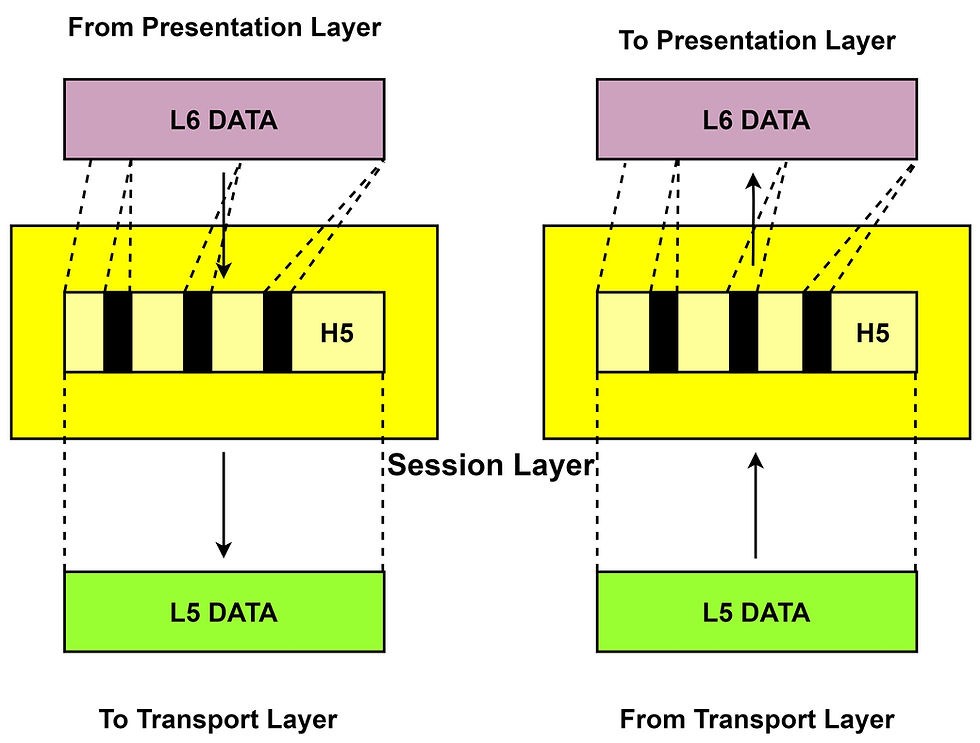
Presentation Layer:
The presentation layer converts the received data from one format to another format. It also shows concern over syntax and semantics while an exchange of data between the system. Hence this layer is also called a translational layer or syntax layer. The functions of the #presentation layer are:
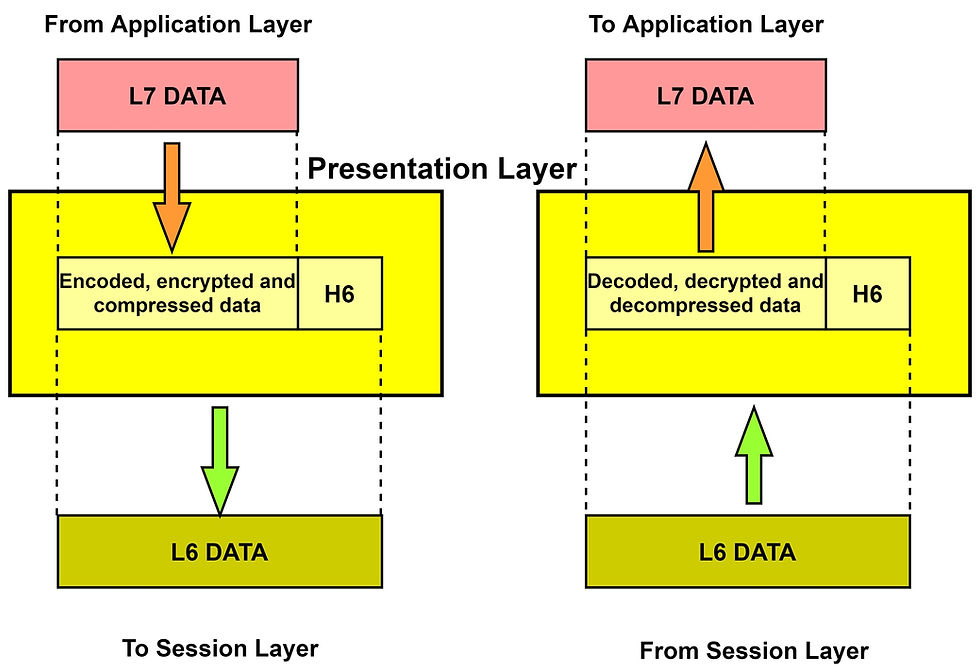
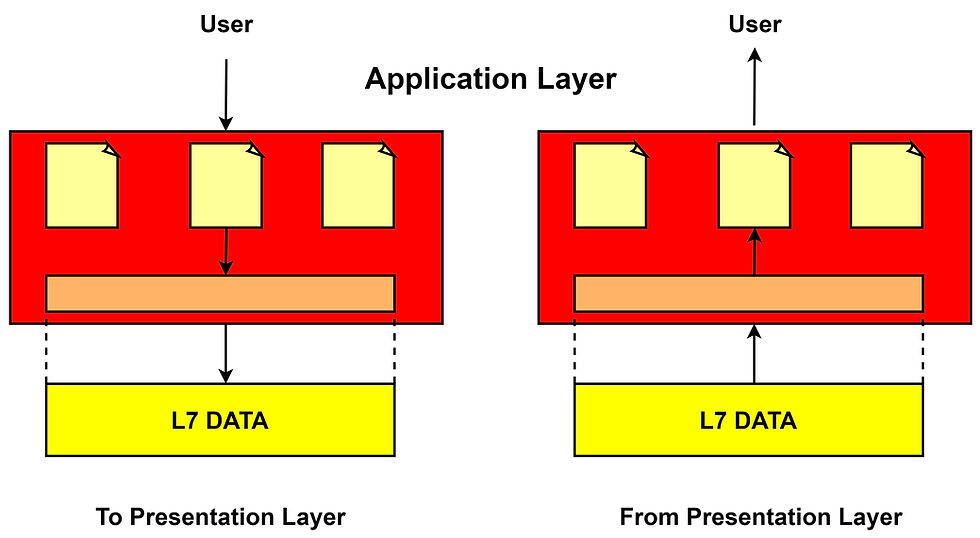
Application Layer:
The application layer is closest to the end-user in which it has straight contact with the software application. It allows the user to access the network services and solves the issues regarding the transparency of the network, resource allocation, synchronizes #communication, etc. It also acts as a window application and displays the received data to the users. for example, #Google Chrome, #Internet Explorer, #Firefox, etc. The various functions of the Application layer are:
Mail services,
Directory services,
File server management, etc.
Thus the OSI reference Model helps us to understand how communication is created between the computing devices across the network with open interoperability and without causing any error by focusing only on the data management.
See also:
Order Electronics Projects
Want us to guide you through your project or make the project for you? Click on the button below or reach out to us via Call/WhatsApp at (+91) - 7600948607
You can -
Order Basic Electronics Projects
Order Embedded Systems Projects
Order IoT Projects
Order FPGA Projects
Order VLSI Projects
Order Image Processing Projects
Order Matlab Projects
Order TinkerCAD Projects
Order Proteus Projects
Click on the button below to fill out the project inquiry form -
Create Various Projects
Check out our Free Arduino Projects Playlist - Arduino Projects
Check out our Free Raspberry Pi Projects Playlist - Raspberry Pi Projects
Check out our Free TinkerCAD Projects Playlist - TinkerCAD Projects
Check out our Free IoT Projects Playlist - IoT Projects
Check out our Free Home Automation Projects Playlist - Home Automation Projects
Check out our Free NodeMCu Projects Playlist - NodeMCu Projects
Follow us -
Please do follow us i.e. #learnelectronicsindia to get daily updates about new blogs, videos, courses, products, offers, competitions, quizzes, and Internship Opportunities.

Informative and concise! LearnElectronics India always delivers quality content.
Wow! This blog on the OSI model by Learn Electronics India is simply outstanding! The way they explain the characteristics, layers, and functions of the OSI model is incredibly clear and informative. It's evident that the author possesses a deep understanding of the subject matter. I've been trying to wrap my head around this topic for a while, and this article has been a game-changer for me. Kudos to the writer for making complex concepts so approachable. I'll definitely be sharing this gem with my fellow tech enthusiasts.